Preclinical studies on CurCousin® underscore its diverse health benefits. These span metabolic health—including body weight, liver vitality, dysbiosis, and lipid balance—as well as notable advantages for joint and bone well-being
Management of Metabolic Imbalances
a) Managing Healthy Body Weight
High caloric diets and inactive lifestyles lead to excessive fat accumulation in adipocytes in the form of triglycerides, resulting in over weight related health problems. Over weight condition is frequently associated with persistent health concerns including metabolic and vascular changes which predispose to the development of the Metabolic health concerns.
Administration of CurCousin® reduced the differentiation of the fat depositing adipocytes and inhibited lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through decreasing cell numbers. Moreover, CurCousin® induced lipolysis in differentiated adipocytes in high-fat diet mice. CurCousin® is effective in preventing high-fat diet-induced body weight gain and adiposity (Lai et al., 2015).
Continue Reading : doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201400809
b) Promotes Thermogenesis and Corrects Dysbiosis
Lee et al., (2022) in a recent study uncovered further avenues of action of CurCousin® in high-fat diet-induced obesity models. They found that CurCousin® has good thermogenesis function and is a novel microbiota modulator to manage healthy body weight. CurCousin® fed animals, lost not only weight, but showed an increase in Akkermansia species whose population is diminished under obese conditions.
Continue Reading : doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2022.01.001
c) Liver Support
Elevated free fatty acids from adipose tissue and dietary intake are transported to the liver, and it stimulates de novo lipogenesis, ultimately leading to hepatic steatosis or fatty liver. Non-alcoholic fatty liver is a common liver health concern that often co-exists in individuals with excess weight concerns. . In high fat-fed rats, administration of CurCousin® induced lipolysis in differentiated adipocytes.
Administration of CurCousin® resulted significant reduction in
– Hepatic triglycerides
– Lipid accumulation
– Inflammatory infiltration, and
– Ballooning degeneration of the liver
CurCousin® supports healthy weight management and promotes live health. (Lai et al., 2015).
Continue Reading : doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201400809
d)Healthy Lipid Levels
Hyperlipidemia is a condition characterized by high lipid content in blood, especially non-HDL cholesterol and triglycerides, which may increase the risk factors for cardiovascular health.
In animal models, administration of CurCousin® significantly reduced serum levels of total cholesterol and triglycerides in high-fat diet fed mice, indicating the effect of CurCousin® on improving lipid homeostasis caused by the high-fat diet (Lai et al., 2015).
Continue Reading : doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201400809
e) Improved Serum Markers
Adipokines like leptin and adiponectin are the hormones produced by white adipose tissues, which play a pivotal role in the energy homeostasis processes. These adipokines also control metabolism and immunity.
CurCousin® favorably modulates adipokines in high-fat diet fed mice (Figure 2). Notable modulatory properties of CurCousin® included inhibition of leptin production, increase in adiponectin expression, and inhibition of local (adipocyte) and provide balance response to certain pro-inflammatory cytokines, like tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-1ß (Unpublished observation).
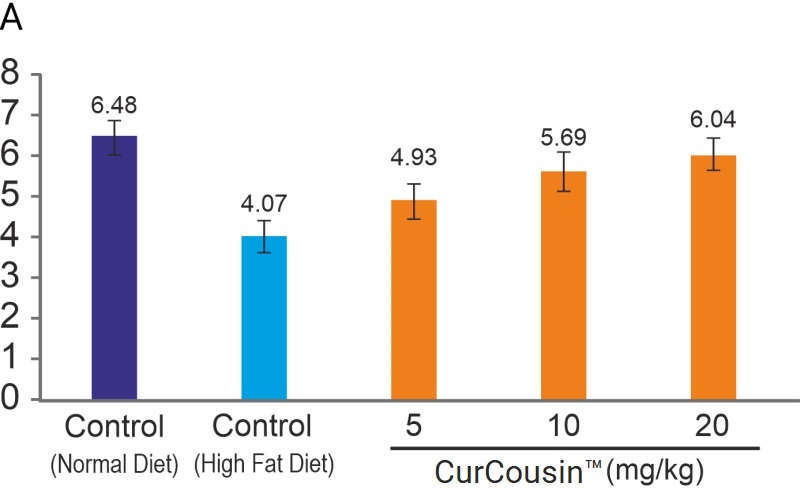
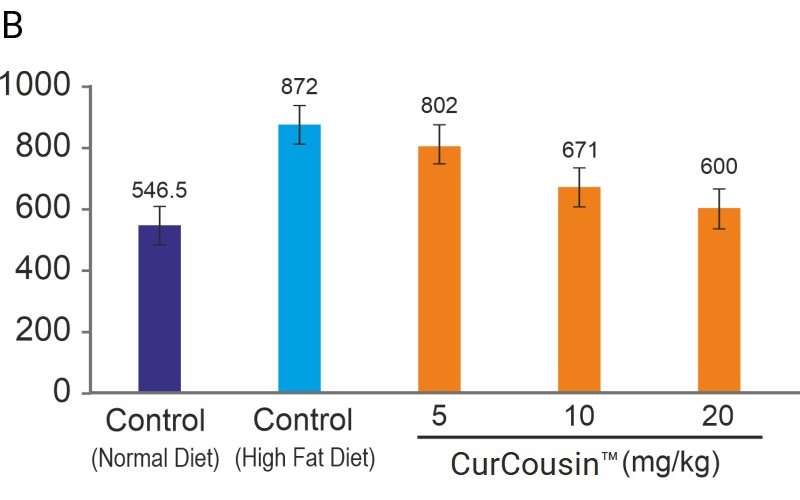
Figure 2: Concentration of (A) adiponectin (ng/ml) (B) leptin (pg/ml) levels in serum of experimental animals
Other Benefits*
a) Supports Bone Health
CurCousin® effectively suppresses osteoclastogenesis via inhibition of the NF-kB signaling pathway as seen in multiple myeloma and breast cancer cells lines, which is mandatory for RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis (Tyagi et al., 2016). Thus, CurCousin® can effectively manage secondary bone lesions associated with postmenopausal bone modifications.
Continue Reading : doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.02.013
b) Joint Health
CurCousin® showed potential protecting activity for mammalian articular cartilage from pathological damages in animal models. For inflammation studies, adjuvant arthritis was induced in Albino Wistar rats of either sex by the injection of heat-killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis and analyzed the effect of CurCousin® in improving paw edema and associated markers. The in vivo studies revealed that CurCousin® significantly reduced acute inflammation and edema in Carrageenan-induced rats (Table 1) (Unpublished observation).
Table 1: Effect of CurCousin® on paw edema in adjuvant-induced arthritic rats
| Test Materials | Doses (mg/kg p.o.) |
%Inhibitory Activity |
|---|---|---|
| CurCousin® | 2.5 | 19.21 % |
| 5 | 37.16 % | |
| 10 | 39.40 % | |
| 20 | 43.44 % | |
| Acetyl salicylic acid (Standard) | 100 | 38.5 % |
Moreover, CurCousin® could effectively modulate the cellular immune system by inhibiting the expression of CD4+ and CD8+ cells and associated cytokines, thus supporting joint health.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, mitigate or prevent any disease.
